Date: 8 (Friday) – 9 (Saturday) December 2023
Venue: Room G42_3.09, Griffith University, Gold Coast, Australia
Organisers: Griffith University, Australia-Korea Foundation (DFAT)
Sponsored by: Embassy of the Republic of Korea in Australia, Austrade, Ubitech Australia

Australia and South Korea (or Korea) are strategic partners with a strong bilateral relationship underpinned by trade and regional strategic interests. South Korea is Australia’s fourth-largest trading partner and fourth-largest export market. 2021 marked the 60th anniversary of diplomatic relations between Australia and Korea. Developing a thriving space sector that can deliver critical capabilities and services is a strategic priority for both governments.
Building on the success of the space events in 2021 and 2022, Griffith University is proud to again be a joint organiser of the Australia-Korea Space Industry Workshop (AKSW2023) with support of Australia Korea Foundation at the Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade (DFAT), Austrade, KOTRA and the Embassy of the Republic of Korea in Australia. On the first day, industry stakeholders from both countries will present their areas of expertise and the capabilities of their respective enterprises. After the workshop concludes, participants will have the opportunity to attend a networking dinner function. On the second day, networking meetings will be arranged for the companies, and institution/industry tours will also be organised.
(Thursday Dec 7, Afternoon) Industry Tours: (Please contact Jun Jo, j.jo@griffith.edu.au)
- Gilmour Space Technologies (63 Burnside Road, Stapylton)
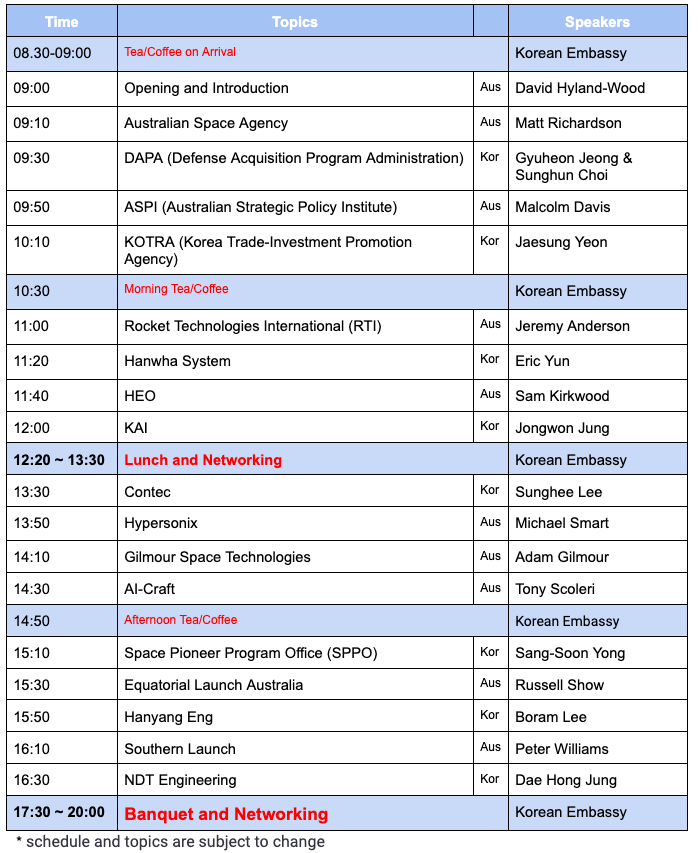
(Friday Dec 8, 2023) Workshop Day
(Saturday Dec 9, 2023) Business Networking Meetings (Contact Jun Jo)
Please refer to the websites:
- Building (G03): https://www.griffith.edu.au/campus-maps/gold-coast-map
- Translink: https://translink.com.au/
Parking information:
Visitor car parking has been arranged for you to park on level 4 of the multistorey car park (G13) located at Griffith University, off Engineering Drive.
Once you enter Engineering Drive, directly to the left of you is the carpark. Continue driving along Engineering Drive by the car park and veer to the left at the first turn which will take you to the car park entrance. At the boom gate, please enter the pin code 546436 followed by the green tick button on the dial pad and the boom gate will open. Please park in one of the bays, 05 ~ 19, on level 4:
If you have any problems with entering the car park, please contact security on 5552 7777 and advise them that a parking space has been reserved for you in ‘Car Park G13’ and they will give you access to the car park by remotely lifting the boom gate.
Dinner:
- Jasmine Room Chinese Cuisine,
- Sundale, level 1/2 Como Cres, Southport QLD 4215
(next to Meriton Hotel and Woolworths)
- We will arrange car sharing from Griffith University to the restaurant.
Please let me know if you need a lift but haven’t heard from us by lunchtime.
Travel Information
Option 1: 12월 8일 AKSW2023만 참석하시는 경우
항공: 인천에서 Brisbane으로 저녁 8시경에 출발하는 대한항공 직통 비행기가 있습니다 (9시간소요)
공항에서 Gold Coast로: 브리스벤공항에서 골드코스트까지는 약 75km입니다.
- 공항에서 기차를 타시면 1시간20분후 Hellensvale역에 도착하시는데, 여기서 시내 Tram으로 갈아타시면 Griffith대학교나 시내로 가실수 있습니다. 기차나 Tram은 한 Line 만 있기 때문에 간단합니다.
- 공항에서 uber나 택시를 타시면 1시간 걸리는데, 호주화 $160정도 나옵니다.
- 호텔은 Southport (대학교 근처)나 Surfers Paradise (시내중심) 또는 Broadbeach에 있는 호텔로 정하시면 Tram으로 모두 연결되어 있어서 이동하시기 편하십니다.
Option 2: 시드니에서 12월 6일에 열리는 스페이스포럼을 들러서 오시는 경우
항공: 인천에서 시드니로 저녁 8시경에 출발하는 대한항공 직통 비행기가 있습니다 (10시간30분소요)
- 시드니에서 골드코스트(OOL) 공항으로 오는 직통 비행기를 타시면 1시간 30 조금 덜 걸립니다.
- 7일오후에 Gilmour Space Technologies에 들르시는 경우는 브리스벤(BNE) 공항으로 오시는 것이 좋습니다.
공항에서 호텔까지는 약 20-30km 떨어져 있는데 우버나 버스등으로 움직이실수 있습니다.
Photos
AKSW2023: Summaries of the presentations in alphabetical order.
AICRAFT
The presentation detailed AICRAFT’s development of low-power smart computing systems for onboard machine learning on satellites. It highlighted their products, such as the Pulsar family, for 1U to 6U and larger satellites, emphasising efficiency, scalability, and single framework development. The presentation discussed the company’s compliance with manufacturing standards and the Australian Defence Industry Security Program. It also included information on product specifications, quantization requirements, and applications like real-time ship localization and cloud coverage estimation, demonstrating their effectiveness in various scenarios.
ASPI
The presentation discussed Australia’s evolving role in space, emphasising the importance of strategic, multinational partnerships, particularly with South Korea. It highlighted the establishment of the Australian Space Agency and Defence Space Command, the development of a commercial space sector, and the significance of sovereign space launch capabilities. The presentation also addressed Australia’s space future, the challenges and opportunities in 2023, and the role of ASPI in shaping space policy and security discussions.
Contec
This presentation detailed the operations of CONTEC, a global leader in Ground Station as a Service (GSaaS) and satellite image services. It covered their business model, core technologies, and partnerships. The presentation included an overview of CONTEC’s ground station services, satellite image pre-processing and applications, and future plans. It outlined the company’s vision for business expansion, emphasising its capabilities in satellite data downlink, processing, application platforms, and ground station design, implementation, and operation services. The presentation also showcased CONTEC’s global reach and its strategic approach to the space industry.
DAPA
The presentation included information on South Korea’s defence budget for 2023, focusing on force improvement, commissioned tasks, force employment, and capability maintenance. The presentation also detailed DAPA’s Defense Space Program, which included projects related to surveillance, reconnaissance, communication satellites, and space weather forecasting. There was a specific focus on projects like the ISR Satellite, Military Communication Satellite-II, and LEO Satellite Communication System. The presentation also discussed international cooperation in space technology and plans for a shared space launch site in Australia.
ELA
ELA presented an overview of Equatorial Launch Australia’s (ELA) spaceport at the Arnhem Space Centre. It detailed the local infrastructure suitable for rocket launches, including large docks, airport facilities, and a nearby hospital. The presentation also highlighted the low maritime and air traffic, making the location ideal for space operations. ELA’s growth plans, phase 2 development for orbital launches, and long-term business strategies were discussed. It mentioned opportunities for collaboration, particularly with Korean partners, and outlined services ELA could provide in the space industry.
Gilmour Space Technologies
Gilmour Space Technologies is an Australian company involved in the space industry. The presentation covered various aspects of the company’s operations, including their work on launching satellites to Low Earth Orbit (LEO) using their Eris Block 1 Rocket. It detailed the company’s R&D, manufacturing, and launch capabilities, highlighting their achievements in developing hybrid rocket technologies and 3D printed rocket fuel. Additionally, it outlined plans for future satellite launches and provided information about their satellite bus and payload missions. The presentation was marked as confidential and included several slides with detailed information about the company’s technology, launch vehicles, and satellite capabilities.
HEO
The presentation outlined the services of HEO, a company specialising in Non-Earth Imaging (NEI) using space-based sensors. NEI captured high-resolution images of spacecraft in orbit, requiring rapid and precise coordination between satellites. HEO offered solutions for automated satellite-to-satellite imaging and boasted a large dataset for machine learning to optimise imaging opportunities. Their services catered to defence, intelligence, commercial, and civil government sectors, focusing on surveillance, asset resilience, and space sustainability. The presentation also discussed their innovative imaging systems, like Holmes and Adler, designed for in-orbit satellite inspection.
KAI
The presentation provided an overview of Korea Aerospace Industries Ltd.’s (KAI) involvement in the space industry. It detailed the company’s history, capabilities, and key projects in satellite technology and space business. The presentation highlighted KAI’s participation in national space endeavours, development of various satellite systems (like KOMPSAT and CAS series), and their recent initiatives in satellite imaging services. Additionally, it outlined KAI’s strategic approach to capturing upcoming space business opportunities and its technological advancements in the field.
Kotra
The presentation primarily focused on advanced communication technologies, particularly the development and application of 5G and 6G networks. It included detailed discussions on various aspects such as 6G terrestrial network concepts, AI-based spectrum sharing, deployable private 5G networks, and non-terrestrial networks, including LEO satellite-based systems. The presentation also covered technological trends, tactical application in defence, and key players and projects in the field. Emphasis was placed on the convergence of communication and computing, highlighting the future direction and potential applications of these emerging technologies.
RTI
Rocket Technologies International (RTI) are creating rocket testing and launch services for the space and defence sectors. Operating the only commercial static rocket test site in Australia, RTI offers horizontal and vertical testing up to 1MN thrust load and for a variety of fuel types. RTI offers high altitude airborne diagnostics for launch and re-entry vehicles and is currently setting up launch services in Australia.
Southern Launch
The presentation was about Southern Launch’s bespoke launch services for space missions. It outlined the company’s unique value proposition, including launch window availability, flexibility in scheduling, and support for just-in-time operations. The presentation highlighted the Whalers Way Orbital Launch Complex, emphasising its low air and maritime traffic, favourable year-round weather conditions, and comprehensive logistical support. Additionally, it covered the company’s expertise in organising launch licensing, managing launch logistics, and providing ground system requirements. The presentation also described the capabilities of the Whalers Way and Koonibba Test Range, including details on launch azimuths, infrastructure, and regulatory compliance.
